Hearing Assessments
What is a hearing test?
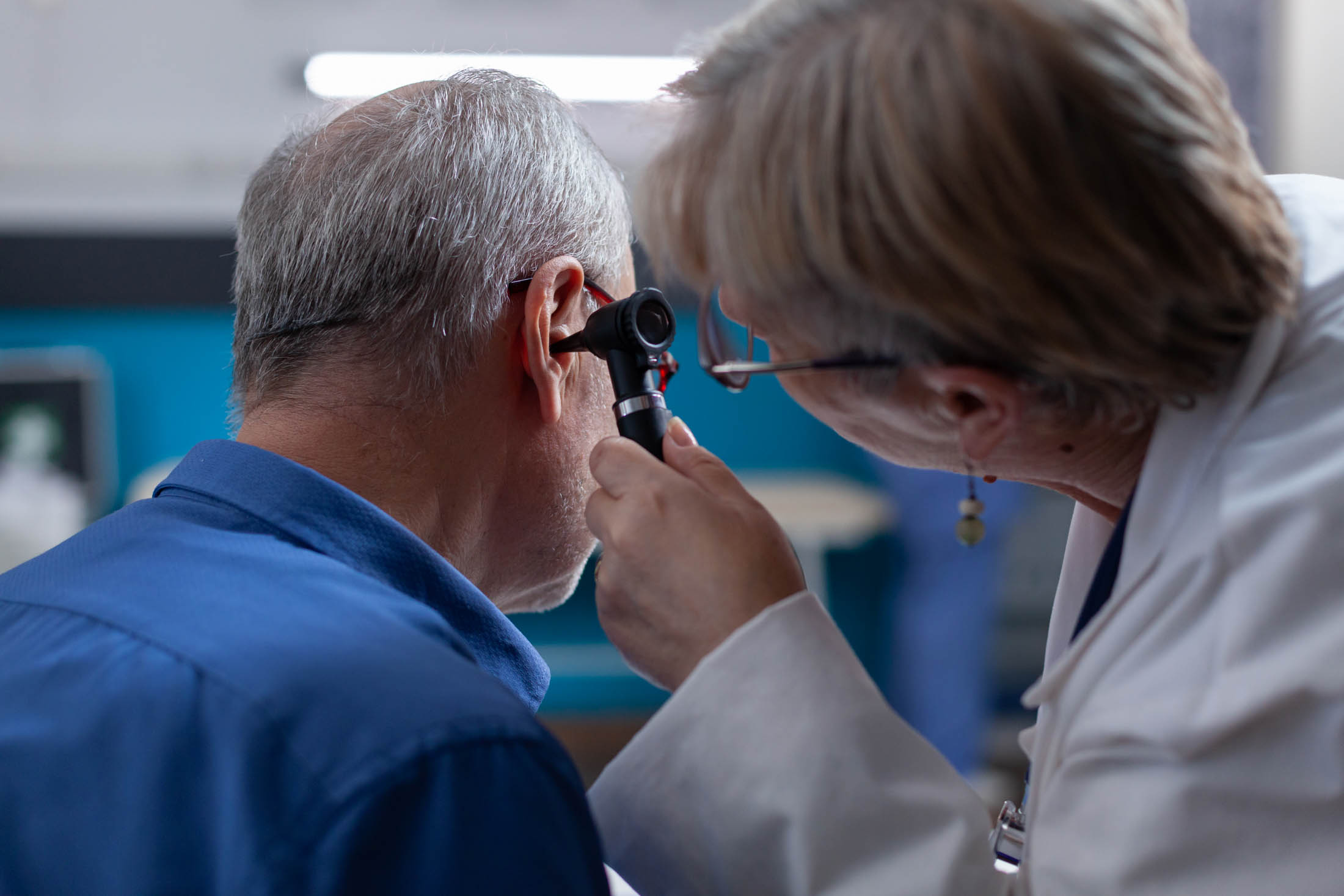
A hearing test is a thorough evaluation conducted by a Qualified Audiologist to assess an individual’s hearing ability. The process begins with a consultation to discuss medical history and any hearing-related symptoms. The audiologist then performs a physical examination of the ears using an otoscope to check for issues such as earwax buildup or infections.
The primary goal of the hearing test is to determine the degree of hearing loss, identifying how severe it is and which types of sounds the individual may struggle with. This includes pure-tone audiometry, where the patient listens to sounds at various pitches and volumes, and speech audiometry to assess the ability to hear and understand speech. Tympanometry may also be conducted to evaluate eardrum movement and detect any middle ear issues.
In addition to determining the degree of hearing loss, the test also identifies the nature of the loss—whether it is due to a medical condition requiring intervention or another underlying cause. Once the audiologist has a complete understanding of the patient’s hearing, they will explain the findings in a clear and meaningful way. A personalized pathway of action will be recommended, which may include hearing aids, medical treatments, or additional diagnostic testing.
The goal of a hearing test is to provide a tailored solution that improves the patient’s hearing ability and overall quality of life.
What happens during a hearing test?
During a hearing test, the audiologist reviews your medical history and examines your ears with an otoscope to check for blockages or abnormalities. Key tests include pure-tone audiometry, where you respond to tones at different pitches and volumes, and speech audiometry, which assesses your ability to hear and understand speech. Additional assessments, such as bone conduction testing and tympanometry, may be used to evaluate middle ear function. Once the tests are complete, the audiologist explains the results, identifies any hearing loss, and recommends appropriate treatment options.
Hearing Assessment Battery
Hearing tests are essential for identifying the degree of hearing loss and the nature (or cause) an individual’s hearing loss. The degree and nature of a loss need to be understood so we can progress to the optimal intervention. This may be a medical pathway from a General Practitioner, an Ear, Nose and Throat specialist or may require aural rehabilitation such as hearing aids, ALDs or cochlear implants. Some classic examples of tests you may experience with the Audiologist at Hearing Help include (but are not limited to);
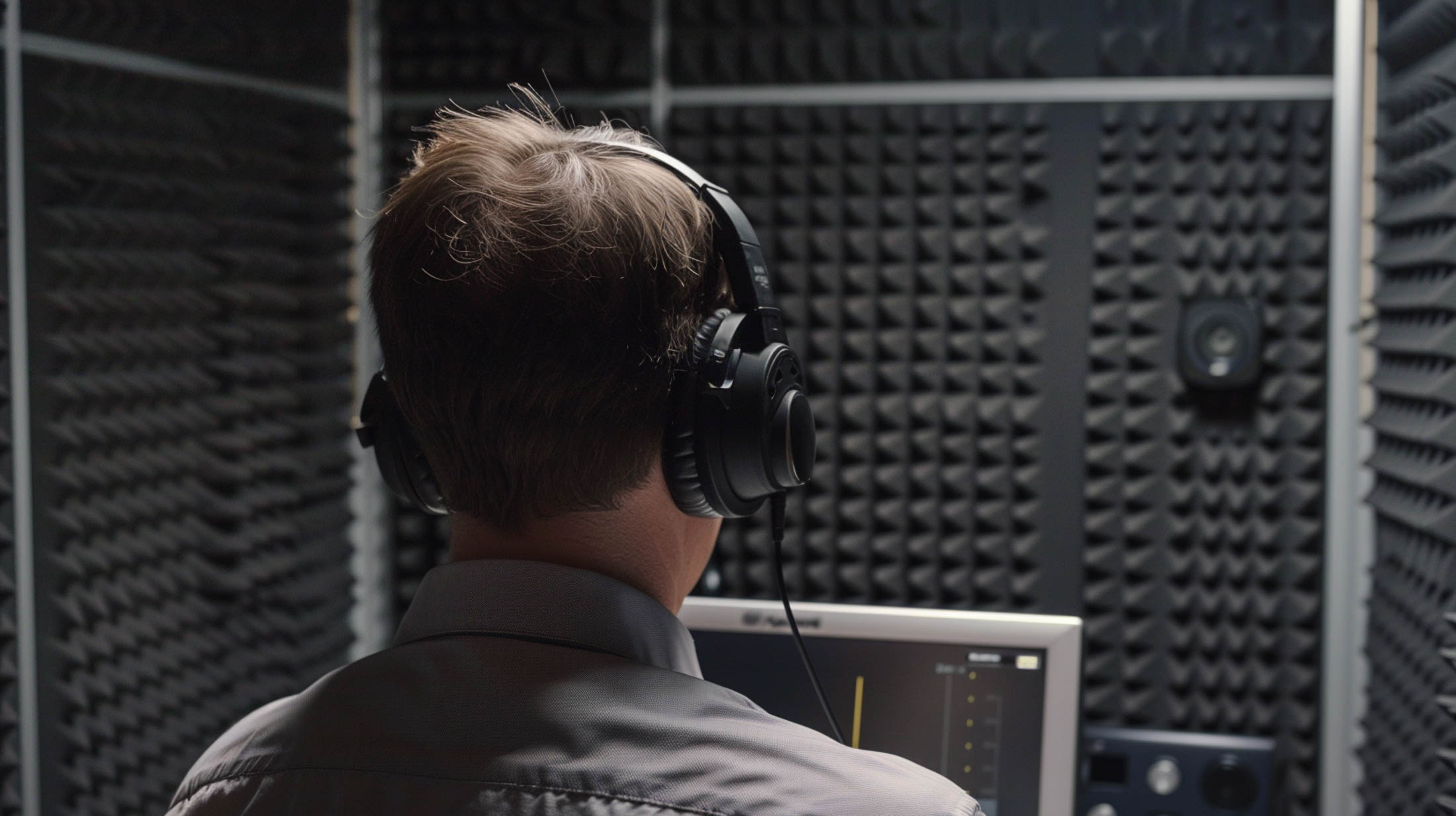

01. Pure Tone Audiometry
This is the most common type of hearing test. It involves using an audiometer to deliver sounds at various pitches and volumes into the ears through headphones. The person being tested responds to each sound, helping to map out their hearing thresholds across different frequencies.
02. Speech Audiometry
This test measures how well a person can hear and understand speech. It involves listening to spoken words at different volumes, which helps to assess the clarity of hearing.
03. Tympanometry
This test evaluates the function of the middle ear by measuring its response to pressure changes. It helps to identify issues like fluid in the ear, ear infections, or eardrum perforations.
04. Acoustic Reflexes
The Acoustic Reflexes test measures the involuntary muscle contraction of the middle ear in response to loud sounds, helping to diagnose hearing and auditory nerve issues.
05. Speech-in-Noise
A Speech Assessment in Background Noise test evaluates an individual’s ability to understand speech in noisy environments, helping to diagnose and manage hearing impairments by measuring speech recognition thresholds in the presence of background noise.
06. Eustachian Tube Dysfunction Test
A Eustachian Tube Dysfunction Test evaluates the function of the Eustachian tube to diagnose and assess any blockage or abnormality affecting middle ear pressure regulation.
